About this topic
Healthy eating is an important part of keeping your diabetes in control. A balanced diet along with your diabetic drugs will help you control your blood sugar. The right portions of healthy foods may help keep your sugar within your goal range. It may also help to lower or maintain your weight, manage cholesterol, the amount of fat in your blood, and blood pressure.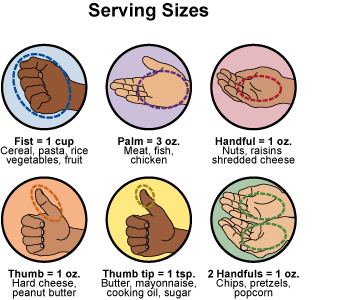
Image(s)
What will the results be?
Healthy eating may help you lower your blood sugar and keep it in a safe range. Keeping your blood sugar in a safe range may lower your chances for long term problems from your diabetes. You may be less likely to have damage to your kidneys, heart, eyes, or nerves.
What changes to diet are needed?
Healthy eating means:
- Eating a range of foods from all food groups.
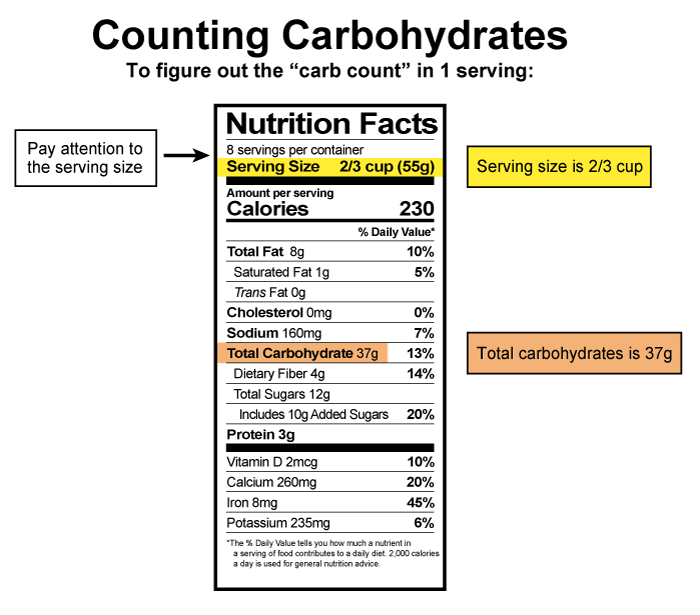
- Eating the right size portions. Read the nutrition facts on each food you eat.
- Eating meals and snacks at the same time each day. Do not skip a meal or snack. Skipping meals may cause your blood sugar to go too low, especially if you are on drugs for your diabetes. Skipping meals can also cause you to eat too much at the next meal.
Talk to your diabetes educator about making a personal meal plan for you. They can also help you eat the foods you like by modifying them to be healthier.
Who should use this diet?
This diet is helpful to people with high blood sugar or diabetes.
What foods are good to eat?
It is important to make a healthy meal. Eat a variety of different foods in the right portion.
- Fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables. Non-starchy vegetables include: Broccoli, green beans, carrots, greens (collard, kale, mustard, turnip), onions, tomatoes, asparagus, beets, cauliflower, celery, and cucumber. Non-starchy vegetables are high in fiber and low in carbohydrates. These will help keep you full for longer without raising your blood sugar.
- Fill 1/4 of your plate with carbohydrates. Try to choose whole grain options. Whole-grain products have more fiber which will make you feel full. Carbohydrates include: Bread, rice, pasta, and starchy vegetables. Starchy vegetables include beans, potatoes, acorn squash, butternut squash, corn, and peas.
- Fill 1/4 of your plate with protein. Choose low-fat cuts of meat like boneless, skinless chicken breast; pork loin; 90% lean beef; lean and skinless turkey meat; and fresh fish (not fried) such as tuna, salmon, or mackerel.
- Add a low-fat or non-fat dairy product like 8 ounces (240 mL) of 1% or skim milk or 6 ounces (180 mL) of low-fat yogurt. Eat the recommended serving. Milk and yogurt have carbohydrates which raise your blood sugar.
- Add a small piece of fruit or 1/2 cup (120 grams) of frozen or canned fruit. Choose canned fruits in juice or water. Fruits include apples, bananas, peaches, pears, pineapple, plums, and oranges. Eat the recommended serving. Fruit has carbohydrates which can raise your blood sugar.
- Include healthy fats in your meal like olive oil, canola oil, avocado, and nuts.
Other good foods to include in your diet are:
- Foods high in fiber. Adding fiber to your meals may help control your blood sugar and cholesterol levels. It may also help with weight loss and prevent belly problems. If you are younger than 50, it is recommended to get 25 to 38 grams per day. If you are older than 50, it is recommended to get 21 to 30 grams per day. Good sources of fiber include:
- Nuts and seeds
- Beans, peas, and other legumes
- Whole-grain products
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Smart snacks in the right portion. Do not go too long in between meals. Ask your dietitian when you should have a snack in between your meals. Snack on things like:
- Nuts
- Vegetables and low-fat dressing
- Light popcorn
- Low-fat cheese and crackers
- 1/2 sandwich
What foods should be limited or avoided?
You may need to limit the amount of some foods you eat and how often you eat them. Foods that should be limited include:
- High fat or processed foods like:
- Bacon
- Sausage
- Hot dogs
- Whole-fat dairy products
- Potato chips
- Foods high in sodium like:
- Canned soups
- Soy sauce and some salad dressings
- Cured meats
- Salted snack foods like pretzels
- Olives
- Fats and oils like:
- Margarine
- Salad dressing
- Gravy
- Lard or shortening
- Foods high in sugar like:
- Candy
- Cookies
- Cake
- Ice cream
- Table sugar
- Soda
- Juice drinks
- Starches that are not whole grain like:
- White rice
- French fries
- White pasta
- White bread
- Sugary cereals
- Baked goods, pastries, croissants
- Beer, wine, and mixed drinks (alcohol). Drink alcohol in moderation (1 drink per day or less for adult women and 2 drinks per day or less for adult men). Drinking alcohol can cause fluctuations in your blood sugar and interfere with how your diabetic drugs work. Talk to your doctor about how you can safely include alcohol into your diet.
What can be done to prevent this health problem?
Some people have a higher chance of developing diabetes than others. This is a life-long problem. You can still lead a normal life. Diabetes can be managed through diet, exercise, and drugs. It is important to have support from your family and friends to help you with your goals.
When do I need to call the doctor?
- Blood sugar level is above 240 mg/dL for more than a day
- Blood sugar level drops to less than 40 and does not respond to 15 grams of simple carbohydrate, like 4 glucose tablets or 1/2 cup (120 mL) of fruit juice
- Trouble breathing
- Very sleepy and trouble concentrating
- Feeling very thirsty
- Needing to urinate (pee) more than normal
- Throw up more than once or have many loose stools
- You are so sick you cannot eat or drink
- Fever over 101°F (38°C)
- Questions about your diet plan
- You are not feeling better in 2 to 3 days or you are feeling worse
Helpful tips
- Plan ahead. Plan your meals and grocery list before going to the store. This will help you to choose foods that are good for you.
- Pack a lunch. Take healthy meals and snacks with you to work.
- Keep a food journal to help keep you on track. Take note of foods that keep your blood sugar in goal range. Also note foods and meals that raise or lower your blood sugar. There are apps for your phone that can help with this.
- Visit a restaurant’s website before eating out. You can see the menu options and nutritional facts. This way, you can see which items best fit into your diet plan. Call ahead if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer:This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. It is not meant to be comprehensive and should be used as a tool to help the user understand and/or assess potential diagnostic and treatment options. It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a specific patient. It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider’s examination and assessment of a patient’s specific and unique circumstances. Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications. This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. UpToDate, Inc. and its affiliates disclaim any warranty or liability relating to this information or the use thereof. The use of this information is governed by the Terms of Use, available at https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/know/clinical-effectiveness-terms
Retrieved from Digital Health Architect on: November 9, 2023
Last Reviewed Date: March 18, 2021
Copyright © 2023 UpToDate, Inc. and its affiliates and/or licensors. All rights reserved.

